Autodidact
a person of great or varied learning
Wednesday, May 7, 2014
European Driving License Quick Reference
My quick reference list of questions for Driving License Theory Test
Distances:
- Parking 5meter Before Pedestrian Crossing / Junctions - Forbidden
- Minimum distance a vehicle must leave clear in front of Traffic lights - 10 Meters
- Minimum distance to park at bus stops - 15 Meters
- Minimum stopping distance before St. Andrews Cross in build-up Area – 5 Meters
- Minimum stopping distance before St. Andrews Cross outside build-up Area – 50 Meters
- Minimum distance between right-edge of the Road and boundary – 3 Meters
- Maximum Height Load extending on the Back - 1.5 meters
- Maximum stopping distance if the visibility is X meters - X/2
- Maximum Centrifugal force with speed doubles at bends - 4 Times
- If double the speed you are travelling the breaking distance is – 4 Times
- The Minimum safe distance behind a vehicle – 2 Seconds
- Maximum Stop Distance with running speed = Reaction Distance + Breaking Distance (With 2 seconds Response)
a. Reaction Distance = (Speed in Km/H / 10 )
* 3
b. Breaking Distance = (Speed in Km/H / 10 ) * (Speed in Km/H / 10
)
c. Breaking Distance = { (Speed in
Km/H /
10 ) * (Speed in Km/H / 10 ) } :2
evasive breaking on dry, even and asphalted road
- On Wet Roads the Stopping distance = 2 * Normal Stopping Distance
- On ICY / Snow Roads the Stopping Distance = 10 * Normal Stopping Distance
- A Single-Axle trailer has actual weight of X kgs. Minimum load of trailer – 4% (600 kgs = 24 Kgs)
- Permissible top speed in built-up areas - 50 km/h
- Maximum speed with permissible mass of 3.0t on Autobahns – 80 km/h
- Maximum speed with permissible mass of 3.0t with trailer on country roads – 80 km/h
- Driving ban on Sunday and Public Holidays – Trucks with trailers & Trucks total mass exceeding 7.5 ft.
- Load allowed to project over the front of vehicle – 50cms project with 2.5 ft height
- One drop of oil can pollute how many liters of water – 600 liters
- Which Permissible mass allowed to park on designated parking areas – 2.8t
Directions
- Right Before Left - Cross Roads & Junctions (Irrespective of Vehicle)
- Vehicle with Blue Light & Siren – Move on to Payment and give way to Vechicle
- Vehicle with Blue Light without Siren - Closed Envoy or Vehicle on Duty
- Vehicle with Amber Light - Large Transport vehicle with low speed / exceptionally Wide Vehicle / Dangers at work or scene of accident
- Priority road - You have the right-of-way at all junctions on this road until cancelled by a "Give Way", "Stop", or "End of Priority Road" sign; outside of urban areas, parking is prohibited on this road
Tuesday, May 14, 2013
Program Run Commands
Program Run Command
Accessibility Controls = access.cpl
Accessibility Wizard = accwiz
Add Hardware Wizard = hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs = appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools = control admintools
Adobe Acrobat ( if installed ) = acrobat
Adobe Distiller ( if installed ) = acrodist
Adobe ImageReady ( if installed ) = imageready
Adobe Photoshop ( if installed ) = photoshop
Automatic Updates = wuaucpl.cpl
Basic Media Player = mplay32
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard = fsquirt
Calculator = calc
Ccleaner ( if installed ) = ccleaner
C: Drive = c:
Certificate Manager = cdrtmgr.msc
Character Map = charmap
Check Disk Utility = chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer = clipbrd
Command Prompt = cmd
Command Prompt = command
Component Services = dcomcnfg
Computer Management = compmgmt.msc
Compare Files = comp
Control Panel = control
Create a shared folder Wizard = shrpubw
Date and Time Properties = timedate.cpl
DDE Shares = ddeshare
Device Manager = devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel ( if installed ) = directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter = dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility = cleanmgr
Disk Defragment = dfrg.msc
Disk Partition Manager = diskmgmt.msc
Display Properties = control desktop
Display Properties = desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected ) = control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility = drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility = verifier
Ethereal ( if installed ) = ethereal
Event Viewer = eventvwr.msc
Files and Settings Transfer Tool = migwiz
File Signature Verification Tool = sigverif
Findfast = findfast.cpl
Firefox = firefox
Folders Properties = control folders
Fonts = fonts
Fonts Folder = fonts
Free Cell Card Game = freecell
Game Controllers = joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor ( xp pro ) = gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game = mshearts
Help and Support = helpctr
Hyperterminal = hypertrm
Hotline Client = hotlineclient
Iexpress Wizard = iexpress
Indexing Service = ciadv.msc
Internet Connection Wizard = icwonn1
Internet Properties = inetcpl.cpl
Internet Setup Wizard = inetwiz
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) = ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) = ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) = ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) = ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) = ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) = ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) = ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) = ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel ( if installed ) = jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel ( if installed ) = javaws
Keyboard Properties = control keyboard
Local Security Settings = secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups = lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out of Windows = logoff
Malicious Software Removal Tool = mrt
Microsoft Access ( if installed ) = access.cpl
Microsoft Chat = winchat
Microsoft Excel ( if installed ) = excel
Microsoft Diskpart = diskpart
Microsoft Frontpage ( if installed ) = frontpg
Microsoft Movie Maker = moviemk
Microsoft Management Console = mmc
Microsoft Narrator = narrator
Microsoft Paint = mspaint
Microsoft Powerpoint = powerpnt
Microsoft Word ( if installed ) = winword
Microsoft Syncronization Tool = mobsync
Minesweeper Game = winmine
Mouse Properties = control mouse
Mouse Properties = main.cpl
MS-Dos Editor = edit
MS-Dos FTP = ftp
Nero ( if installed ) = nero
Netmeeting = conf
Network Connections = control netconnections
Network Connections = ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard = netsetup.cpl
Notepad = notepad
Nview Desktop Manager ( if installed ) = nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager = packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbccp32
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard = osk
Opens AC3 Filter ( if installed ) = ac3filter.cpl
Outlook Express = msimn
Paint = pbrush
Password Properties = password.cpl
Performance Monitor = perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor = perfmon
Phone and Modem Options = telephon.cpl
Phone Dialer = dialer
Pinball Game = pinball
Power Configuration = powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes = control printers
Printers Folder = printers
Private Characters Editor = eudcedit
Quicktime ( if installed ) = quicktime.cpl
Quicktime Player ( if installed ) = quicktimeplayer
Real Player ( if installed ) = realplay
Regional Settings = intl.cpl
Registry Editor = regedit
Registry Editor = regedit32
Remote Access Phonebook = rasphone
Remote Desktop = mstsc
Removable Storage = ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests = ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy ( xp pro ) = rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras = sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks = control schedtasks
Security Center = wscui.cpl
Services = services.msc
Shared Folders = fsmgmt.msc
Sharing Session = rtcshare
Shuts Down Windows = shutdown
Sounds Recorder = sndrec32
Sounds and Audio = mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game = spider
SQL Client Configuration = clicongf
System Configuration Editor = sysedit
System Configuration Utility = msconfig
System File Checker Utility ( Scan Immediately ) = sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility ( Scan Once At Next Boot ) = sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility ( Scan On Every Boot ) = sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility ( Return to Default Settings) = sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility ( Purge File Cache ) = sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility ( Set Cache Size to Size x ) = sfc /cachesize=x
System Information = msinfo32
System Properties = sysdm.cpl
Task Manager = taskmgr
TCP Tester = tcptest
Telnet Client = telnet
Tweak UI ( if installed ) = tweakui
User Account Management = nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager = utilman
Volume Serial Number for C: = label
Volume Control = sndvol32
Windows Address Book = wab
Windows Address Book Import Utility = wabmig
Windows Backup Utility ( if installed ) = ntbackup
Windows Explorer = explorer
Windows Firewall = firewall.cpl
Windows Installer Details = msiexec
Windows Magnifier = magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure = wmimgmt.msc
Windows Media Player = wmplayer
Windows Messenger = msnsgs
Windows Picture Import Wizard (Need camera connected) = wiaacmgr
Windows System Security Tool = syskey
Windows Script host settings = wscript
Widnows Update Launches = wupdmgr
Windows Version ( shows your windows version ) = winver
Windows XP Tour Wizard = tourstart
Wordpad = write
Zoom Utility = igfxzoom
Accessibility Controls = access.cpl
Accessibility Wizard = accwiz
Add Hardware Wizard = hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs = appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools = control admintools
Adobe Acrobat ( if installed ) = acrobat
Adobe Distiller ( if installed ) = acrodist
Adobe ImageReady ( if installed ) = imageready
Adobe Photoshop ( if installed ) = photoshop
Automatic Updates = wuaucpl.cpl
Basic Media Player = mplay32
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard = fsquirt
Calculator = calc
Ccleaner ( if installed ) = ccleaner
C: Drive = c:
Certificate Manager = cdrtmgr.msc
Character Map = charmap
Check Disk Utility = chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer = clipbrd
Command Prompt = cmd
Command Prompt = command
Component Services = dcomcnfg
Computer Management = compmgmt.msc
Compare Files = comp
Control Panel = control
Create a shared folder Wizard = shrpubw
Date and Time Properties = timedate.cpl
DDE Shares = ddeshare
Device Manager = devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel ( if installed ) = directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter = dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility = cleanmgr
Disk Defragment = dfrg.msc
Disk Partition Manager = diskmgmt.msc
Display Properties = control desktop
Display Properties = desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected ) = control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility = drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility = verifier
Ethereal ( if installed ) = ethereal
Event Viewer = eventvwr.msc
Files and Settings Transfer Tool = migwiz
File Signature Verification Tool = sigverif
Findfast = findfast.cpl
Firefox = firefox
Folders Properties = control folders
Fonts = fonts
Fonts Folder = fonts
Free Cell Card Game = freecell
Game Controllers = joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor ( xp pro ) = gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game = mshearts
Help and Support = helpctr
Hyperterminal = hypertrm
Hotline Client = hotlineclient
Iexpress Wizard = iexpress
Indexing Service = ciadv.msc
Internet Connection Wizard = icwonn1
Internet Properties = inetcpl.cpl
Internet Setup Wizard = inetwiz
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) = ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) = ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) = ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) = ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) = ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) = ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) = ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) = ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel ( if installed ) = jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel ( if installed ) = javaws
Keyboard Properties = control keyboard
Local Security Settings = secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups = lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out of Windows = logoff
Malicious Software Removal Tool = mrt
Microsoft Access ( if installed ) = access.cpl
Microsoft Chat = winchat
Microsoft Excel ( if installed ) = excel
Microsoft Diskpart = diskpart
Microsoft Frontpage ( if installed ) = frontpg
Microsoft Movie Maker = moviemk
Microsoft Management Console = mmc
Microsoft Narrator = narrator
Microsoft Paint = mspaint
Microsoft Powerpoint = powerpnt
Microsoft Word ( if installed ) = winword
Microsoft Syncronization Tool = mobsync
Minesweeper Game = winmine
Mouse Properties = control mouse
Mouse Properties = main.cpl
MS-Dos Editor = edit
MS-Dos FTP = ftp
Nero ( if installed ) = nero
Netmeeting = conf
Network Connections = control netconnections
Network Connections = ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard = netsetup.cpl
Notepad = notepad
Nview Desktop Manager ( if installed ) = nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager = packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbccp32
ODBC Data Source Administrator = odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard = osk
Opens AC3 Filter ( if installed ) = ac3filter.cpl
Outlook Express = msimn
Paint = pbrush
Password Properties = password.cpl
Performance Monitor = perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor = perfmon
Phone and Modem Options = telephon.cpl
Phone Dialer = dialer
Pinball Game = pinball
Power Configuration = powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes = control printers
Printers Folder = printers
Private Characters Editor = eudcedit
Quicktime ( if installed ) = quicktime.cpl
Quicktime Player ( if installed ) = quicktimeplayer
Real Player ( if installed ) = realplay
Regional Settings = intl.cpl
Registry Editor = regedit
Registry Editor = regedit32
Remote Access Phonebook = rasphone
Remote Desktop = mstsc
Removable Storage = ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests = ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy ( xp pro ) = rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras = sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks = control schedtasks
Security Center = wscui.cpl
Services = services.msc
Shared Folders = fsmgmt.msc
Sharing Session = rtcshare
Shuts Down Windows = shutdown
Sounds Recorder = sndrec32
Sounds and Audio = mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game = spider
SQL Client Configuration = clicongf
System Configuration Editor = sysedit
System Configuration Utility = msconfig
System File Checker Utility ( Scan Immediately ) = sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility ( Scan Once At Next Boot ) = sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility ( Scan On Every Boot ) = sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility ( Return to Default Settings) = sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility ( Purge File Cache ) = sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility ( Set Cache Size to Size x ) = sfc /cachesize=x
System Information = msinfo32
System Properties = sysdm.cpl
Task Manager = taskmgr
TCP Tester = tcptest
Telnet Client = telnet
Tweak UI ( if installed ) = tweakui
User Account Management = nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager = utilman
Volume Serial Number for C: = label
Volume Control = sndvol32
Windows Address Book = wab
Windows Address Book Import Utility = wabmig
Windows Backup Utility ( if installed ) = ntbackup
Windows Explorer = explorer
Windows Firewall = firewall.cpl
Windows Installer Details = msiexec
Windows Magnifier = magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure = wmimgmt.msc
Windows Media Player = wmplayer
Windows Messenger = msnsgs
Windows Picture Import Wizard (Need camera connected) = wiaacmgr
Windows System Security Tool = syskey
Windows Script host settings = wscript
Widnows Update Launches = wupdmgr
Windows Version ( shows your windows version ) = winver
Windows XP Tour Wizard = tourstart
Wordpad = write
Zoom Utility = igfxzoom
Monday, December 3, 2012
Commands for System Statistics (UNIX)
Regular Resource Monitoring UNIX Commands:
1. iostat
2. free
3. mpstat
4. sar
4. ps -aux
5. ps -eo pcpu,pid,user,args | sort -r -k1 | less
6. ps -eo pid,pcpu,comm
7.ps -eo pid,pcpu,user,cmd | awk '{if ($3 == "h06adm") print }'
8. fdisk -l | grep Disk - Display total hard disk size
9. df -h - Display disk free in Human understandable format (In GB)
10. cat /proc/cpuinfo ( To check the CPU Core)
11. lscpu (to check the cpu)
12. /hwinfo - To get hardware details
13. /usr/sbin/dmidecode - To get the internals of hardware
14. cat /proc/meminfo or free -g (To check Ram)
15. Sed (2/String1/String2) - String editor to replae
16. mpstat -p All - To check each core of cpu
1. iostat
2. free
3. mpstat
4. sar
4. ps -aux
5. ps -eo pcpu,pid,user,args | sort -r -k1 | less
6. ps -eo pid,pcpu,comm
7.ps -eo pid,pcpu,user,cmd | awk '{if ($3 == "h06adm") print }'
8. fdisk -l | grep Disk - Display total hard disk size
9. df -h - Display disk free in Human understandable format (In GB)
10. cat /proc/cpuinfo ( To check the CPU Core)
11. lscpu (to check the cpu)
12. /hwinfo - To get hardware details
13. /usr/sbin/dmidecode - To get the internals of hardware
14. cat /proc/meminfo or free -g (To check Ram)
15. Sed (2/String1/String2) - String editor to replae
16. mpstat -p All - To check each core of cpu
Example shell Program:
#!/bin/sh
ps -eo pid,pcpu,comm | awk '{if ($2 > 4) print }' >> ~/ps_eo_test.txt
#!/bin/bash
# by Paul Colby (http://colby.id.au), no rights reserved ;)
PREV_TOTAL=0
PREV_IDLE=0
while true; do
CPU=(`cat /proc/stat | grep '^cpu '`) # Get the total CPU statistics.
unset CPU[0] # Discard the "cpu" prefix.
IDLE=${CPU[4]} # Get the idle CPU time.
# Calculate the total CPU time.
TOTAL=0
for VALUE in "${c...@]}"; do
let "TOTAL=$TOTAL+$VALUE"
done
# Calculate the CPU usage since we last checked.
let "DIFF_IDLE=$IDLE-$PREV_IDLE"
let "DIFF_TOTAL=$TOTAL-$PREV_TOTAL"
let "DIFF_USAGE=(1000*($DIFF_TOTAL-$DIFF_IDLE)/$DIFF_TOTAL+5)/10"
echo -en "\rCPU: $DIFF_USAGE% \b\b"
# Remember the total and idle CPU times for the next check.
PREV_TOTAL="$TOTAL"
PREV_IDLE="$IDLE"
# Wait before checking again.
sleep 1
done
Secure Copy of UNIX
Example syntax for
Secure Copy (scp)
What is Secure Copy?
scp allows files to be
copied to, from, or between different hosts. It uses ssh for
data transfer and provides the same authentication and same level of security
as ssh.
Examples
Copy the file "foobar.txt" from a
remote host to the local host
|
$ scp your_username@remotehost.edu:foobar.txt
/some/local/directory
|
Copy the file "foobar.txt" from the
local host to a remote host
|
$ scp foobar.txt
your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory
|
Copy the directory "foo" from the
local host to a remote host's directory "bar"
|
$ scp -r foo
your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory/bar
|
Copy the file "foobar.txt" from remote
host "rh1.edu" to remote host "rh2.edu"
|
$ scp your_username@rh1.edu:/some/remote/directory/foobar.txt
\
your_username@rh2.edu:/some/remote/directory/ |
Copying the files "foo.txt" and
"bar.txt" from the local host to your home directory on the remote
host
|
$ scp foo.txt bar.txt your_username@remotehost.edu:~
|
Copy the file "foobar.txt" from the
local host to a remote host using port 2264
|
$ scp -P 2264 foobar.txt
your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory
|
Copy multiple files from the remote host to your
current directory on the local host
|
$ scp
your_username@remotehost.edu:/some/remote/directory/\{a,b,c\} .
|
|
$ scp your_username@remotehost.edu:~/\{foo.txt,bar.txt\} .
|
Monday, August 13, 2012
HANA Features
Features of HANA (Hybrid In-Memory Database):
No Disk

In-Memory Computing
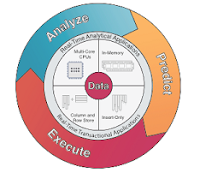 High performance
in-memory computing will change how enterprises work. Currently, enterprise
data is split into two databases for performance reasons. Disk-based
row-oriented database systems are used for operational data (e.g. "insert
or update a specific sales order") and column-oriented databases are used
for analytics (e.g. “sum of all sales in China grouped by product”). While
analytical databases are often kept in-memory, they can also be mixed with
disk-based storage media.
High performance
in-memory computing will change how enterprises work. Currently, enterprise
data is split into two databases for performance reasons. Disk-based
row-oriented database systems are used for operational data (e.g. "insert
or update a specific sales order") and column-oriented databases are used
for analytics (e.g. “sum of all sales in China grouped by product”). While
analytical databases are often kept in-memory, they can also be mixed with
disk-based storage media.
Read more at http://www.no-disk.com/
Active and Passive Data Store
 By default, all data is
stored in-memory to achieve high-speed data access. However, not all data is
accessed or updated frequently and needs to reside in-memory, as this increases
the required amount of main memory unnecessarily. This so-called historic or
passive data can be stored in a specific passive data storage based on less
expensive storage media, such as SSDs or hard disks, still providing sufficient
performance for possible accesses at lower cost. The dynamic transition from
active to passive data is supported by the database, based on custom rules
defined as per customer needs.
By default, all data is
stored in-memory to achieve high-speed data access. However, not all data is
accessed or updated frequently and needs to reside in-memory, as this increases
the required amount of main memory unnecessarily. This so-called historic or
passive data can be stored in a specific passive data storage based on less
expensive storage media, such as SSDs or hard disks, still providing sufficient
performance for possible accesses at lower cost. The dynamic transition from
active to passive data is supported by the database, based on custom rules
defined as per customer needs.
We define two categories of data stores:
active and passive: We refer to active data when it is accessed frequently and
updates are expected (e.g., access rules). In contrast, we refer to passive
data when this data either is not used frequently and neither updated nor read.
Passive data is purely used for analytical and statistical purposes or in
exceptional situations where specific investigations require this data. A possible storage hierarchy is given by memory registers,
cache memory, main memory, flash storages, solid state disks, SAS hard disk
drives, SATA hard disk drives, tapes, etc. As a result, rules for migrating
data from one store to another need to be defined, we refer to it as aging
strategy or aging rules. The process of aging data, i.e. migrating it from a
faster store to a slower one, is considered as background tasks, which occurs
on regularly basis, e.g. weekly or daily. Since this process involves
reorganization of the entire data set, it should be processed during times with
low data access, e.g. during nights or weekends.
Combined Row and Column
StoreTo support analytical and transactional workloads, two different types of database systems evolved. On the one hand, database systems for transactional workloads store and process every day’s business data in rows, i.e. attributes are stored side-by-side. On the other hand, analytical database systems aim to analyze selected attributes of huge data sets in a very short time.
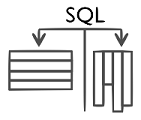 Column and row-oriented
storage in HANA provides the foundation to store data according to its frequent
usage patterns in column or in row-oriented manner to achieve optimal
performance. Through the usage of SQL, that supports column as well as
row-oriented storage, the applications on top stay oblivious to the choice of
storage layout.
Column and row-oriented
storage in HANA provides the foundation to store data according to its frequent
usage patterns in column or in row-oriented manner to achieve optimal
performance. Through the usage of SQL, that supports column as well as
row-oriented storage, the applications on top stay oblivious to the choice of
storage layout.
Minimal Projections
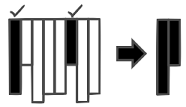 To increase the overall
performance, it is required to select only the minimal set of attributes that
should be projected for each query. This has two important advantages: First,
it dramatically reduces the amount of accessed data that is transferred between
client and server. Second, it reduces the number of accesses to random memory
locations and thus increases the overall performance
To increase the overall
performance, it is required to select only the minimal set of attributes that
should be projected for each query. This has two important advantages: First,
it dramatically reduces the amount of accessed data that is transferred between
client and server. Second, it reduces the number of accesses to random memory
locations and thus increases the overall performanceAny Attribute as an Index
 Traditional row-oriented
databases store tables as collections of tuples. To improve access to specific
values within columns and to avoid scanning the entire table, that is, all
columns and rows, indexes are typically created for these columns. The offsets of the matching
values are used as an index to retrieve the values of the remaining attributes,
avoiding the need to read data that is not required for the result set.
Consequently, complex objects can be filtered and retrieved via any of their
attributes.
Traditional row-oriented
databases store tables as collections of tuples. To improve access to specific
values within columns and to avoid scanning the entire table, that is, all
columns and rows, indexes are typically created for these columns. The offsets of the matching
values are used as an index to retrieve the values of the remaining attributes,
avoiding the need to read data that is not required for the result set.
Consequently, complex objects can be filtered and retrieved via any of their
attributes.Insert-only
 Insert-only or append-only
describes how data is managed when inserting new data. The principle idea of
insert-only is that changes to existing data are handled by appending new
tuples to the data storage. Insert-only enables storing
the complete history of value changes and the latest value for a certain
attribute.For the history-based
access control, insert-only builds the basis to store the entire history of
queries for access decision. In addition, insert-only enables tracing of access
decision, which can be used to perform incident analysis
Insert-only or append-only
describes how data is managed when inserting new data. The principle idea of
insert-only is that changes to existing data are handled by appending new
tuples to the data storage. Insert-only enables storing
the complete history of value changes and the latest value for a certain
attribute.For the history-based
access control, insert-only builds the basis to store the entire history of
queries for access decision. In addition, insert-only enables tracing of access
decision, which can be used to perform incident analysis Group-Key
 A common access pattern of
enterprise applications is to select a small group of records from larger
relations. To speed up such queries,
group-key indexes can be defined that build on the compressed dictionary. A
group key index maps a dictionary-encoded value of a column to a list of
positions where this value can be found in a relation.
A common access pattern of
enterprise applications is to select a small group of records from larger
relations. To speed up such queries,
group-key indexes can be defined that build on the compressed dictionary. A
group key index maps a dictionary-encoded value of a column to a list of
positions where this value can be found in a relation. No Aggregate Tables
Given the incredible aggregation speed provided by HANA, all aggregates required by any application can now be computed from the source data on-the-fly, providing the same or better performance as before and dramatically decreasing code complexity which makes system maintenance a lot easier.
On-the-fly Extensibility
 The possibility of adding
new columns to existing database tables dramatically simplifies a wide range of
customization projects. In a column store database,
such as HANA, all columns are stored in physical separation from one another.
This allows for a simple implementation of column extensibility, which does not
need to update any other existing columns of the table. This reduces a schema
change to a pure metadata operation, allowing for flexible and real-time schema
extensions.
The possibility of adding
new columns to existing database tables dramatically simplifies a wide range of
customization projects. In a column store database,
such as HANA, all columns are stored in physical separation from one another.
This allows for a simple implementation of column extensibility, which does not
need to update any other existing columns of the table. This reduces a schema
change to a pure metadata operation, allowing for flexible and real-time schema
extensions. Reduction of Layers
 To avoid redundant data,
logical layers, describing the transformations, are executed during runtime,
thus increasing efficient use of hardware resources by removing all
materialized data maintenance task. Moving formalizable application logic to
the data it operates on results in a smaller application stack and increases
maintainability by code reduction. (Use Stored Procedures & other Business Fuction Libraries)
To avoid redundant data,
logical layers, describing the transformations, are executed during runtime,
thus increasing efficient use of hardware resources by removing all
materialized data maintenance task. Moving formalizable application logic to
the data it operates on results in a smaller application stack and increases
maintainability by code reduction. (Use Stored Procedures & other Business Fuction Libraries)
Partitioning
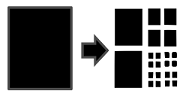 We distinguish between two
partitioning approaches: vertical and horizontal partitioning, whereas a
combination of both approaches is also possible. Vertical partitioning refers
to the rearranging of individual database columns. It is achieved by splitting
columns of a database table into two or more column sets. Each of the column
sets can be distributed on individual databases servers. This can also be used
to build up database columns with different ordering to achieve better search
performance while guaranteeing high-availability of data. In contrast, horizontal
partitioning addresses large database tables and how to divide them into
smaller pieces of data. As a result, each piece of the database table contains
a subset of the complete data within the table. Splitting data into equivalent
long horizontal partitions is used to support search operations and better
scalability.
We distinguish between two
partitioning approaches: vertical and horizontal partitioning, whereas a
combination of both approaches is also possible. Vertical partitioning refers
to the rearranging of individual database columns. It is achieved by splitting
columns of a database table into two or more column sets. Each of the column
sets can be distributed on individual databases servers. This can also be used
to build up database columns with different ordering to achieve better search
performance while guaranteeing high-availability of data. In contrast, horizontal
partitioning addresses large database tables and how to divide them into
smaller pieces of data. As a result, each piece of the database table contains
a subset of the complete data within the table. Splitting data into equivalent
long horizontal partitions is used to support search operations and better
scalability.Lightweight Compression
 For in-memory databases, compression is
applied to reduce the amount of data that is transferred between main memory
and CPU, as well as to reduce overall main memory consumption. However, the
more complex the compression algorithm is, the more CPU cycles it will take to
decompress the data to perform query execution. As a result, in-memory
databases choose a trade-off between compression ration and performance using
so called light-weight compression algorithms.
For in-memory databases, compression is
applied to reduce the amount of data that is transferred between main memory
and CPU, as well as to reduce overall main memory consumption. However, the
more complex the compression algorithm is, the more CPU cycles it will take to
decompress the data to perform query execution. As a result, in-memory
databases choose a trade-off between compression ration and performance using
so called light-weight compression algorithms.Bulk Load
 Besides transactional
inserts, HANA also supports a bulk load mode. This mode is designed to insert
large sets of data without the transactional overhead and thus enables
significant speed-ups when setting up systems or restoring previously collected
data.
Besides transactional
inserts, HANA also supports a bulk load mode. This mode is designed to insert
large sets of data without the transactional overhead and thus enables
significant speed-ups when setting up systems or restoring previously collected
data.Multi-core and Parallelization
 A CPU core can be considered as single worker
on a construction area. If it is possible to map each query to a single core,
the system’s response time is optimal. Query processing also involves data
processing, i.e. the database needs to be queried in parallel, too. If the
database is able to distribute the workload across multiple cores of a single
system, this is optimal. If the workload exceeds physical capacities of a
single system, multiple servers or blades need to be involved for work
distribution to achieve optimal processing behavior. From the database
perspective, the partitioning of data sets enables parallelization since
multiple cores across servers can be involved for data processing.
A CPU core can be considered as single worker
on a construction area. If it is possible to map each query to a single core,
the system’s response time is optimal. Query processing also involves data
processing, i.e. the database needs to be queried in parallel, too. If the
database is able to distribute the workload across multiple cores of a single
system, this is optimal. If the workload exceeds physical capacities of a
single system, multiple servers or blades need to be involved for work
distribution to achieve optimal processing behavior. From the database
perspective, the partitioning of data sets enables parallelization since
multiple cores across servers can be involved for data processing.
MapReduce
 MapReduce is a programming
model to parallelize the processing of large amounts of data. HANA emulates the MapReduce
programming model and allows the developer to define map functions as
user-defined procedures. Support for the MapReduce programming model enables
developers to implement specific analysis algorithms on HANA faster, without
worrying about parallelization and efficient execution by HANA’s calculation
engine.
MapReduce is a programming
model to parallelize the processing of large amounts of data. HANA emulates the MapReduce
programming model and allows the developer to define map functions as
user-defined procedures. Support for the MapReduce programming model enables
developers to implement specific analysis algorithms on HANA faster, without
worrying about parallelization and efficient execution by HANA’s calculation
engine.Dynamic Multithreading within Nodes
partitioning database tasks
on large data sets into as many jobs as threads are available on a given node.
This way, the maximal utilization of any supported hardware can be achieved.
Single and Multi-Tenancy

Analytics on Historical
Data
For analytics the historical data is the key. In HANA, historical data is
instantly available for analytical processing from solid state disk (SSD)
drives. Only active data is required to reside in-memory permanently.
Text Retrieval and
Exploration

Elements of search in unstructured data, such as linguistic or fuzzy search find their way into the domain of structured data, changing system interaction. Furthermore, for business environments added value lies in combining search in unstructured data with analytics of structured data.
Object Data Guides
The in-memory database improves the retrieving performance of a business object by adding
 which is called object data guide and includes
two aspects: In addition to the parent instance, every node instance can
contain the link to the corresponding root instance. Using this additional
attribute, it is possible to retrieve all nodes in parallel instead of waiting
for the information from the parent level. Additionally, each node type in a
business object can be numbered. Then, for every root instance, a bit vector
(Object Data Guide) is stored, whose bit at position i indicates if an instance
of node number i exists for this root instance. Using this bit vector, a table
only needs to be checked if the corresponding bit is set, reducing the
complexity of queries to a minimum. This is mainly for Sparse tree data.
which is called object data guide and includes
two aspects: In addition to the parent instance, every node instance can
contain the link to the corresponding root instance. Using this additional
attribute, it is possible to retrieve all nodes in parallel instead of waiting
for the information from the parent level. Additionally, each node type in a
business object can be numbered. Then, for every root instance, a bit vector
(Object Data Guide) is stored, whose bit at position i indicates if an instance
of node number i exists for this root instance. Using this bit vector, a table
only needs to be checked if the corresponding bit is set, reducing the
complexity of queries to a minimum. This is mainly for Sparse tree data.Thursday, August 9, 2012
Features of the Column Storage Engine (HANA)
Both the
row and column storage engine each have a built-in query capability optimized
for the respective storage method. Consequently each of the storage engines has
its strengths when used for differing tasks. The row engine supports all
features provided by SAP HANA SQL. The column engine, however, has been
optimized for analytics and supports a narrower set of SQL features. These
features are much faster than the corresponding functions of the row store.
Since not all features provided by SAP HANA SQL are natively supported by the
column engine, the query optimizer sometimes creates an execution plan that
involves both storage engines even if the data reside completely in the column
store. On the other hand it is sometimes desirable to transfer intermediate
results from the row store to the column store because subsequent calculation
steps can be processed much faster there. As a general rule of thumb we
recommend to use the "Explain Plan" feature of the SAP HANA studio to
explore execution of critical SQL statements and optimize the data model and
SQL statements accordingly.
The
following list explains the query features of the column engine. The column
engine can natively execute queries that are logically equivalent to queries
that can be expressed in the following format.
SELECT
FROM
[ WHERE ]
[ GROUP BY ]
[ HAVING ]
[ ORDER BY
ASC | DESC separated by comma> ]
[ LIMIT [OFFSET ] ]
A column
engine FROM specification can be one of the following:
·
·
( SELECT * FROM WHERE
·
INNER
JOIN ON
·
LEFT
OUTER JOIN ON
·
RIGHT
OUTER JOIN ON
·
FULL
OUTER JOIN ON
The column
engine supports following join conditions.
·
=
§ Data types of two columns should be the same. Decimals with different
precisions or scales are also treated as different data types.
·
AND operations
between column engine join conditions
§ For outer joins, cyclical joining is not supported. For example, T.a = S.a AND T.b = R.b is not supported if there is already a join condition between S and R.
The column
engine supports the following filter conditions
·
Binary comparison (=,
<>, <, >, <= and >=) between column engine expressions
·
LIKE, IS NULL and
IN predicate on a column engine expression
·
AND, OR, NOT
operations over column engine filter conditions
The column
engine supports the following scalar expressions.
·
Constant values
·
Binary arithmetic
operation (+, -, * and /) between column engine expressions
·
·
String
concatenation (||) between column engine expressions
·
CASE WHEN THEN
·
expression> ...
[ELSE ] END
·
CASE WHEN
THEN
... [ELSE ] END
·
Functions listed
below with column engine expressions as arguments
§ TO_DECIMAL, TO_NUMBER, TO_BIGINT, TO_REAL, TO_DOUBLE, TO_CHAR,
§ TO_NCHAR, TO_DATE, TO_TIMESTAMP and BINTOHEX/HEXTOBIN
§ Format strings are not supported for TO_CHAR, TO_NCHAR, TO_DATE and
§ TO_TIMESTAMP
§ LTRIM | RTRIM | TRIM, LENGTH, SUBSTR, INSTR and LOWER | UPPER
§ WEEKDAY, DAYS_BETWEEN, SECONDS_BETWEEN, ADD_DAYS, UTCTOLOCAL,
§ LOCALTOUTC, ISOWEEK and QUARTER
§ LN | LOG, EXP | POWER | SQRT, SIN | COS | TAN, ASIN | ACOS | ATAN,
SINH | COSH
§ and FLOOR | CEIL
§ NULLIF, NVL, NVL2 and COALESCE
§ EXTRACT( YEAR | MONTH FROM )
·
Functions without
arguments are evaluated by the SQL parser. The evaluated results are passed to
the column engine as constant values.
§ CURRENT_CONNECTION, CURRENT_SCHEMA, CURRENT_USER, SYSUUID, CURRENT_DATE/
CURRENT_TIME/ CURRENT_TIMESTAMP and CURRENT_UTCDATE/ CURRENT_UTCTIME/
CURRENT_UTCTIMESTAMP
§ Expressions equivalent to one of the listed above (e.g. CAST function)
·
The column engine
supports the following aggregation expressions.
§ MIN | MAX | COUNT | SUM | AVG ([DISTINCT] )
§
Since SQL
provides multiple possible ways to formulate a query, an SQL query that is not
in the above format can be processed natively by the column engine if the query
is equivalent to a query that can be represented in the correct format. Below
are examples of such equivalence. Equivalence is denoted as .
SELECT * FROM T, S WHERE T.a = S.a
.SELECT * FROM T INNER JOIN S ON T.a = S.a
SELECT
DISTINCT a, b, c FROM T
.SELECT a, b, c FROM T GROUP BY a, b, c
SELECT * FROM T WHERE EXISTS (SELECT
* FROM S WHERE T.a = S.a)
.SELECT DISTINCT T.* FROM T INNER JOIN S ON T.a
= S.a
Equivalent only if
table T has a primary key.
SELECT * FROM T WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT
* FROM S WHERE T.a =
S.a)
.SELECT T.* FROM T LEFT OUTER JOIN S ON T.a = S.a WHERE
S.a
IS NULL
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
My quick reference list of questions for Driving License Theory Test Distances: Parking 5meter Before Pedestrian Crossing / Junc...
-
The concept of T-shirt sizes for SAP HANA SAP defined so-called T-shirt sizes for SAP HANA to both simplify the sizing and to limit...
-
Both the row and column storage engine each have a built-in query capability optimized for the respective storage method. Consequently e...





